
The separated charges will create an electric field which will tend to pull the charges back together. It will tend to move negative charge to one end, and leave the other end of the bar with a net positive charge.
#LOOP THE LOOP PHYSICS CALCULATOR FREE#
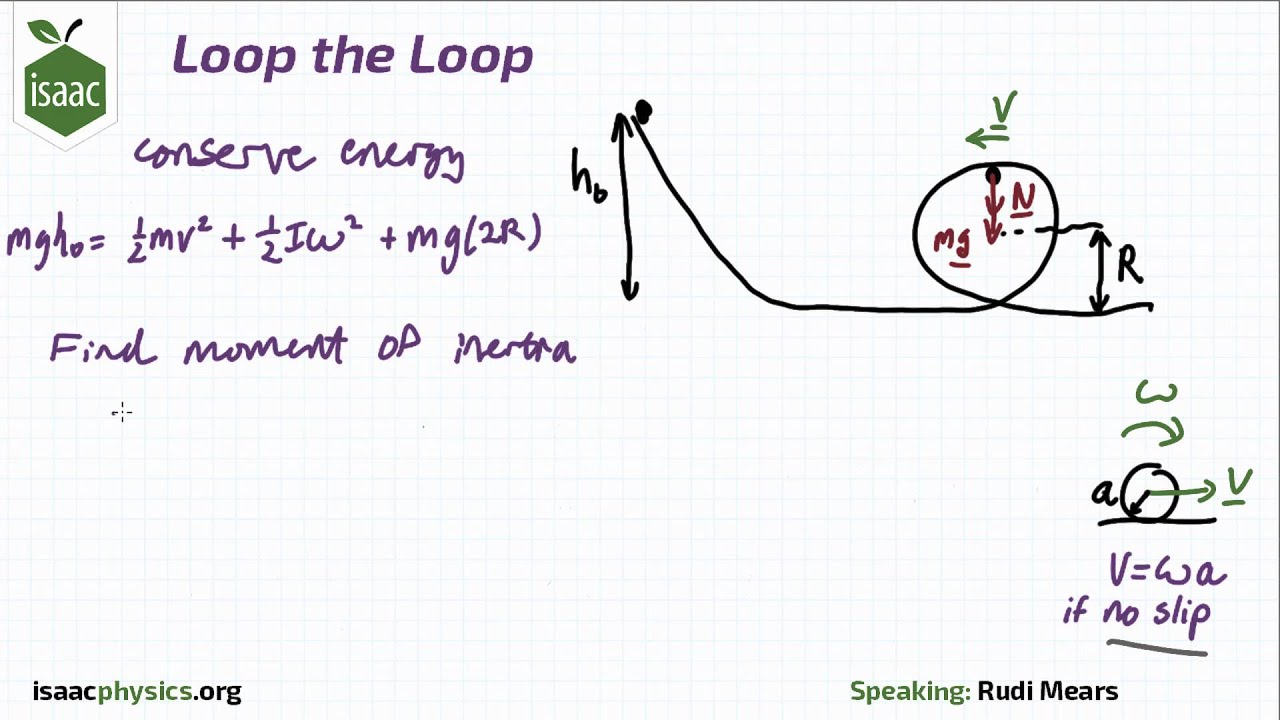
This force will act on free charges in the conductor. The change in the flux is thus equal to its original value,į i = B A cos q = (0.15T) p(0.12m)² = 6.8×10 -3Tm²Įmf = N ( DF / Dt) = (6.8×10 -3Tm²)/(0.20s) = 3.4×10 -2V = 34mV.Īn interesting application of Faraday's law is to produce an emf via motion of the conductor.Īs a simple example, let's consider a conducting bar moving perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field with constant velocity v.įor this first look, we have just a bar, not a complete conducting loop, and we will consider what happens using just the force on a moving charge, F = qvBsin q. When the loop is stretched so that its area is zero, the flux through the loop is zero. This is a case where the change in flux is caused by a change in the area of the loop.īoth the magnetic field and the angle q remain constant. If it takes 0.20s to close the loop, find the magnitude of the average induced emf in it during this time. The loop is grasped at points A and B and stretched until it closes. The flexible loop in Figure P20.10 has a radius of 12cm and is in a magnetic field of strength 0.15T. Magnetic flux is defined in a similar manner to electric flux.įor a loop of wire with area A, in a magnetic field, B, the magnetic flux, F is given by: We quantify the change in terms of magnetic flux. Magnetic flux will play an important role throughout this chapter.Įxperiments in the 19th century showed that a changing magnetic field can produce an emf. In this chapter, we make that connection, seeing how a magnetic field can produce a potential difference.
We have seen that a magnetic field exerts a force on a wire carrying a current, and that a wire carrying a current generates a magnetic field.Ĭurrents are produced by electric fields, so there seems to be some connection between electricity and magnetism.

repulsive when the currents are in opposite directions.attractive when the currents are in the same direction.Force Between Two Wires: F / l = m 0 I 1 I 2 / 2 p d.Torque on a Current Loop: t = B I A sin q.Whenever you get lost or just want to check the results, feel free to use our centripetal force calculator. After rounding to three significant figures, the velocity equals 0.914 m/s. We can also rewrite the result with a different unit.Work out the square root of the previous outcome to get the velocity, v = √9 = 3 ft/s.To do so, multiply both sides of the equation by r and divide by m Rearrange the centripetal force formula to estimate the square of velocity.Let's find the velocity of an object that travels around the circle with radius r = 5 ft when the centripetal force equals 3.6 pdl. We can also write the solution using scientific notation, F = 3.125×10⁴ N, or with a proper suffix, F = 31.25 kN.

Before we do the computations, let's convert the mass to kilograms and switch the speed units from km/h to m/s.
#LOOP THE LOOP PHYSICS CALCULATOR HOW TO#
How to calculate the centripetal force acting on a car that goes around a circular track? The car's mass is 2 t, its velocity equals 45 km/h, and the radius of the track is 10 m: Having the theory in our minds, let's try to solve a few centripetal force examples. How to distinguish between them? Let's take a look at the two diagrams with the comparison of centripetal vs. It isn't always evident whether we're dealing with an inertial or non-inertial frame of reference. The second one is the centrifugal force - the representative of the force of inertia.Īs you can see, the centripetal force is present in both reference frames, while the centrifugal force unveils only in the non-inertial one. Once again, there is the centripetal force acting towards the rotation center. In a non-inertial reference frame (the kid's point of view), there are two corresponding forces of the same values that balance each other. In an inertial reference frame (a parent watching the kid from a distance), there is only one force that changes the movement direction - the centripetal force Imagine a circular motion, e.g., a kid on a merry-go-round: The crucial factor that helps us distinguish between these two is the frame of reference. Our centrifugal force calculator uses precisely the same equation as for the centripetal one: At first glance, it may seem that there is no difference between centripetal and centrifugal force.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
